Carotid stenosis ICD 10 is also known as carotid artery stenosis ICD 10. Before knowing about Carotid Stenosis ICD 10, you need to know what is Carotid Stenosis.
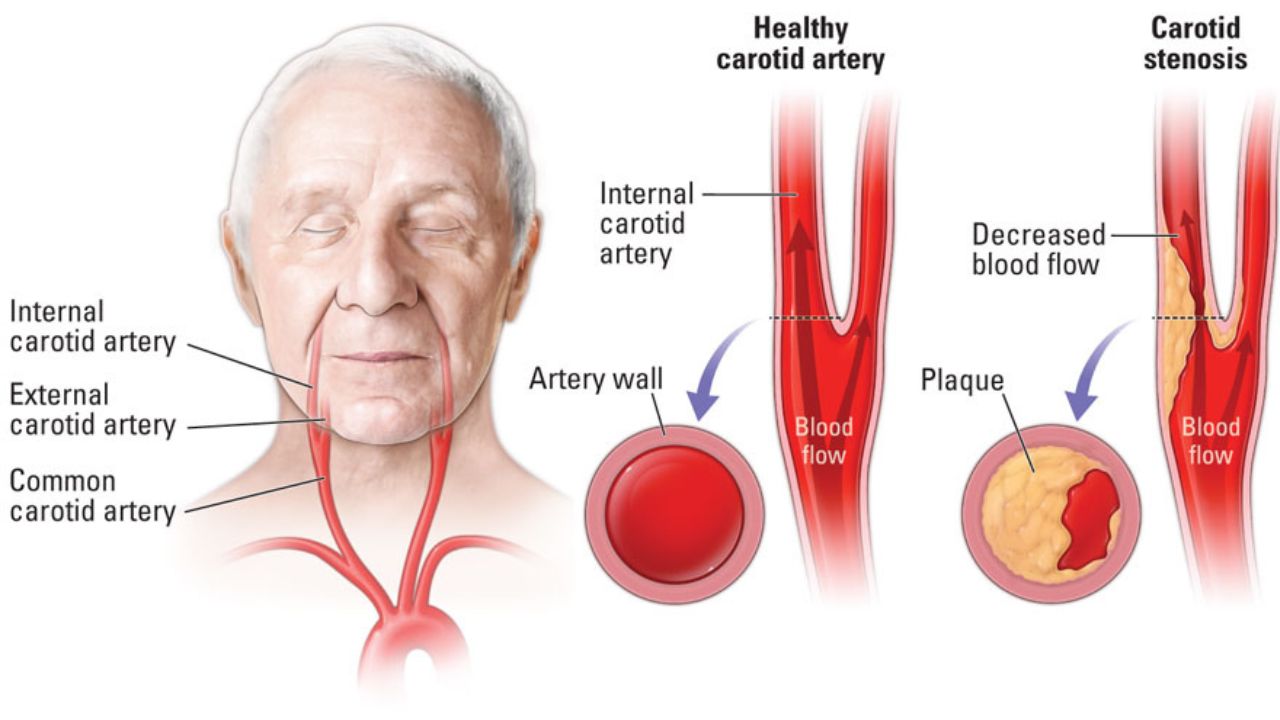
As a carotid stenosis or carotid artery stenosis is the narrowing of the carotid artery is referred to. It occurs especially in old age. The carotid artery narrowing may be asymptomatic but can also lead to a stroke. In some cases, patients need surgery. Read stenosis here, everything Important about the common carotid artery and icd 10 code for carotid stenosis.
Carotid Stenosis ICD 10 : I63 | I64 | I61 | I69 | I65
Carotid artery stenosis: description
As carotid stenosis, doctors refer to a narrowing (stenosis) of the carotid artery. There is a right and a left Common carotid artery (Arteria carotis communis), which run along the sides of the neck from the chest in the direction of the head. They share approximately half the height of the neck in an internal and external carotid artery on (Arteria carotis interna and externa). The Arteria carotis interna (ACI) provides the first line of the brain with blood while the Arteria carotis externa (ACE) of the skin, mainly the head, face and upper neck organs with blood. A carotid artery stenosis is usually located in the area of the bifurcation.
Incidence of carotid artery stenosis
The incidence of carotid artery stenosis increases with age of the patient. For example, is narrowed at only about 0.2 percent of men under 50 in the carotid artery at least half. With over 60 Years of age have up to two per cent and at over 80-Year-old seven percent of such asymptomatic carotid stenosis. Compared to women, men are affected about twice as often.
Carotid artery stenosis: symptoms
The carotid stenosis is often caused for a long time with no symptoms. Doctors speak, then, of an asymptomatic carotid stenosis. If these symptoms occur, they can vary. Example:
- Visual disturbances such as double vision or visual field defects
- Language disorders
- Paralysis of the arms and legs
- Headache
- Vertigo attacks
These internal carotid artery stenosis-symptoms may occur paroxysmally, and for minutes to hours remain the same. When you form back, one also speaks of a transitory ischemic attack (TIA), so a temporary lack of blood flow to the brain going. Should the symptoms over a longer period of time, or even increase, is a stroke.
Causes of carotid artery stenosis
The most common cause for a carotid stenosis is the calcification of the vessels (atherosclerosis). With increasing age deposits (Plaques) are formed on the inner walls of blood vessels – including the carotid artery. These deposits narrow the vessel. Risk factors such as Smoking, high blood pressure or increased blood fats speed up the process. The Plaques can eventually tear off little pieces, with the blood flow in brain vessels and a narrowing or clogging. The result is a decreased or absent blood flow to the brain tissue (ischemia). The downstream brain tissue is not quickly with sufficient oxygen supply, dying off – an ischemic stroke (cerebral infarction) is.
Carotid artery stenosis: risk factors
Various risk factors contribute to a narrowing of the carotid artery. These are, among others:
- Age and gender
- High blood pressure (arterial hypertension)
- Elevated Blood Fats (Hyperlipidemia)
- Diabetes mellitus
- Smoking
- Obesity
The life style has accordingly stenosis is a major influence on the emergence of a common carotid artery. Who eats a healthy diet, sufficient exercise and not Smoking, ill probably rare, or at least later in carotid stenosis as someone who cultivates an unhealthy lifestyle.
Carotid artery stenosis: examinations and diagnosis
A carotid stenosis is noticeable mostly in an ultrasound examination, but in some cases also by typical symptoms. The first point of contact is in the normal case, the family doctor, who will refer you to a neurologist. A doctor asked you first, in detail your medical history. Possible questions include, for example:
- Do you suffer from high blood pressure or Diabetes?
- Do You Smoke?
- You suffer and blurred vision?
Carotid artery stenosis: physical examination
Then the doctor examines you. He felt the pulse at the neck and at the wrists. A carotid stenosis should be present in the section of the common carotid artery, can be, under certain circumstances, the pulse hard palpable. After listening to the doctor, her heart and great vessels with the stethoscope from. In the case of a carotid stenosis flow noise may be via the carotid arteries with an audible click.
Carotid artery stenosis: laboratory tests
The doctor will take a blood sample to the laboratory on blood lipid levels, glucose levels, and coagulation values to be examined to make.
Carotid artery stenosis: technical studies
Especially the ultrasound examination (sonography) is helpful in the diagnosis of carotid stenosis – or, more specifically, a special Form of ultrasound: the duplex sonography. With your help, both the blood flows can be represented in the vessels, as well as the vessels themselves.
Often, Doctors carry out further investigations to be able to the risk of stroke better estimate. This includes the ultrasonic examination of the heart that counts. The doctor can determine if you in the heart clots have formed, which threaten to be in the carotid arteries washed and laid in this.
Furthermore, it is a long-term electrocardiogram (Holter ECG) performed on heart rhythm disorders to find. These increase the risk that blood clots form in the heart, which can lay the carotid arteries.
Possible vasoconstriction in other vessels of the brain provide, to be able to complement the neurologist is often a transcranial Doppler sonography. Here, an ultrasonic device, the flow velocities in the cerebral vessels recorded in the skull run.
May is also an angiography performed. This Vascular imaging to the patient, contrast medium is injected, and the patient’s head x-rayed. The blood vessels filled with contrast, what are the possible narrowing of the visible power.
Sometimes, for this purpose, a computer tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are used.
Treatment for carotid stenosis
The aim of the treatment of a carotid stenosis is to prevent a stroke, and the blood supply to the brain. Therefore, it is important to minimize the risk factors. As a Patient, you can contribute significantly: get Used to a healthy lifestyle with plenty of exercise, a balanced diet and the absence of nicotine.
In Addition, your blood should be set pressure and blood sugar optimally. A healthy lifestyle also helps in this case. If necessary, the physician prescribes you medication (blood pressure lowering, blood sugar-lowering).
To minimize the risk of a stroke, the doctor may prescribe to you also, “blood-thinning tablets”. These so-called platelet aggregation inhibitors (such as acetylsalicylic acid = ASPIRIN) to prevent blood clots (thrombi) to form in the blood vessels clog.
Carotid artery stenosis: operative treatment
Surgery may be indicated in patients who have already suffered a stroke due to carotid artery stenosis or a high risk for a stroke have (for example due to a very strong vasoconstriction, or high Blood fats). In the case of the so-called Thrombendarteriektomie (TEA, also CEA = Carotid Thrombendarteriektomie) is removed, the narrowing under General anesthesia or regional anesthesia: The surgeon makes an incision in the skin of the affected area of the carotid artery and cut you. He removes the deposits on the vessel wall and sews the vessel is then again. The Operation takes about an hour.
There is a risk that the surgery itself is a stroke occurs. Therefore, the procedure should only be performed in medical centers with sufficient experience with TEA. In addition, the Doctors weigh in Use carefully and risks of the Operation carefully. The life expectancy, the degree of stenosis, and any pre-existing conditions play a role.
Another method, in the case of a carotid artery stenosis, is the so-called carotid angioplasty with Stenting. It is made with a balloon catheter in the affected vessel from the inside, stretched, and a stent is inserted, the self-expanding.
Carotid artery stenosis: disease course and prognosis
The carotid stenosis may long remain undetected and cause no symptoms. This is dangerous because, in General, the narrowing of the carotid artery with the time increasing, which increases the risk for a stroke. Annually, about 2 of 100 asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis, which are detected by accident, trigger a stroke. In addition, patients with carotid stenosis have an increased risk of having a heart attack.
So, talk to your doctor in detail about symptoms, causes,treatment options and carotid stenosis icd 10 code. Due to the Change of lifestyle with adequate exercise and healthy eating can the prognosis of carotid stenosis can be improved.