Diabetes mellitus is a pathology that belongs to the group of endocrine pathologies. It is associated with a disorder in the absorption of glucose. The disorder develops due to the absolute or relative insufficiency of insulin – the hormone responsible for its processing. A patient with diabetes mellitus has hyperglycemia.
This condition is characterized by a persistent rise in plasma glucose. The patient has a violation of all types of metabolism: water-salt, carbohydrate, protein, fat, mineral. The disease has a chronic course. Diabetes mellitus belongs to common ailments. It is detected in almost 6% of the world’s population.
Causes of diabetes mellitus
The reasons for the development of types of diabetes of the first and second types in patients are different. The disease of the first type is detected in young patients under thirty years of age. Disruption of insulin production occurs when the pancreas is affected by autoimmune genesis. With it, the destruction of insulin-producing ß-cells occurs.
In most patients, this pathology occurs after a viral infection. Most often, mumps, measles rubella, viral hepatitis. This pathological condition can also develop after toxic effects on the body with the following substances: nitrosamine, pesticides, some drugs.
These substances contribute to the disruption of the immune response and the occurrence of autoimmune reactions. The impact of altered immune cells on the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas causes their death. In this regard, the production of insulin decreases. This condition develops when more than 80% of these cells are affected.
In the second type of disease, all cells become insensitive to insulin. Plasma insulin levels are normal or elevated, but cells do not perceive it. Most of these patients with diabetes. Glucose tolerance occurs for the following reasons:
- Genetic predisposition. These patients have relatives with diabetes. If both parents suffer from it, the likelihood of inheriting a predisposition to it increases to 70%.
- Obesity. With a large amount of adipose tissue in the body, their sensitivity to insulin decreases.
- Poor nutrition. With a predominance of simple carbohydrates in food and a lack of fiber, the risk of developing diabetes is increased.
- Cardiovascular pathology. Severe forms of these diseases – atherosclerosis, ischemic heart disease, arterial hypertension – lead to an increase in tissue insulin resistance.
- Chronic stress. In this state, the level of catecholamines and glucocorticoids increases. This contributes to the development of diabetes.
- Taking certain medications. The group of drugs that increase the risk of diabetes include: synthetic glucocorticoids, diuretics, some antihypertensive drugs, cytostatics.
- Chronic adrenal cortex insufficiency. This disease increases the risk of developing tissue insulin resistance.
As a result, the penetration of glucose into cells decreases and its level in the blood increases.
Symptoms of diabetes mellitus
- insatiable thirst;
- increased urination, leading to dehydration;
- dry mouth;
- increased fatigue;
- general weakness;
- minor skin lesions heal slowly;
- vomit;
- persistent nausea;
- the smell of acetone from the patient;
- increased breathing;
- palpitations;
- itchy skin;
- rapid weight loss;
- frequent urination;
- decreased visual acuity.
If these signs appear, you should see your doctor right away for a blood sugar test.
Types of diabetes
Pathology, depending on the reasons, is divided into several types. The following types of disease are distinguished: type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, specific forms, gestational diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes mellitus
Option 1 type occurs when there is a lack of insulin production in the body. It is a hormone that regulates glucose metabolism in tissues. Lack of it occurs due to damage to the beta cells of the pancreas due to the development of autoimmune reactions.
The immune system is damaged and produces antibodies against the body’s own tissues. This situation arises after the transferred viral infections, severe stress, exposure to other adverse factors.
The disease often occurs in young people and children. The disease has a sudden onset. Its symptoms are pronounced, as cells quickly find themselves in a state of starvation. A very high level of glucose is detected, often it reaches up to 30 mmol / L in the blood.
Variety 1 of the disease is considered LADA-diabetes. This is an autoimmune diabetes that occurs in adults and is characterized by a latent course. For him, a decrease in insulin in the blood and a normal weight are typical.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
In type 2 diabetes, insulin secretion is not affected. There is an excess level of this hormone in the blood. The cells in the body will lose their sensitivity to the action of the substance. Patients develop insulin resistance. About 90% of all identified persons with diabetes are patients with the second type of the disease. This type of diabetes often develops in obese people over the age of 40.
Among the concomitant diseases are revealed: atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension. The disease has a gradual onset. Its symptomatology is scanty. The glucose level rises moderately. Antibodies to pancreatic cells are not detected. This situation contributes to the late visits of the patient to the doctor when complications have appeared.
Complications of diabetes mellitus
Separate acute and chronic complications of the disease. Acute complications develop rapidly and require urgent hospitalization. These include the following conditions:
- Hypoglycemia. In this condition, glucose levels are sharply reduced. It occurs when an overdose of insulin, untimely food intake, physical overstrain. The patient develops hunger, a feeling of trembling in the hands, dizziness, sweating, aggression. Then consciousness is disturbed.
- Ketoacidosis With it, the level of glucose rises. It does not enter cells and accumulates in the blood. The condition is manifested by a decrease in appetite, dry skin, and thirst. The smell of acetone emanates from the patient. Confusion of consciousness, drowsiness appears.
- Hyperosmolar coma. It is characterized by an increase in blood glucose with general dehydration of the body.
- Lactic acidotic coma. The condition occurs in the elderly in the presence of disorders of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems due to oxygen starvation.
Patients with signs of these pathological conditions require immediate medical attention.
With late complications, lesions of the vascular and nervous system are observed. Diabetic angiopathy is a massive vascular lesion. It applies to vessels of any caliber. Microangiopathies cause diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy. Macroangiopathies affect the vessels of the heart, brain and arteries of the lower extremities.
Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
If you suspect this disorder, the following studies are prescribed:
- blood glucose levels;
- urine analysis for glucose and ketone bodies;
- glycosylated hemoglobin test;
- C-peptide in the blood;
- stress test (determination of glucose tolerance).
To identify complications, the following is prescribed: ultrasound scanning of the kidneys, EEG of the brain, rheoencephalography, rheovasography of the vessels of the legs.
Diabetes mellitus treatment
The fulfillment of the doctor’s prescriptions should be strictly observed. Blood sugar control and drug treatment for this disease are carried out for life. These measures slow down the pathological process and avoid complications.
Treatment of pathology involves a decrease in blood glucose, as well as the normalization of metabolism and the prevention of complications.
Diabetes diet
Diet therapy is the mainstay of treatment. The diet is prescribed, taking into account body weight, age, level of physical activity. The patient is taught the principle of calculating the calorie content of dishes, they must contain the required amount of all nutrients.
| What can you eat | What you can’t eat |
|---|---|
| meat | any cereals |
| seafood | potato |
| bird | sugar |
| a fish | confectionery |
| hard cheese | candies |
| eggs | flour products |
| butter | bananas |
| cabbage | corn |
| avocado | cereals |
| zucchini | rice |
| white yogurt without sugar | mayonnaise |
* The table provides an incomplete list of products. For the correct and complete diet, consult a specialist.
The principle of the diet for this disease:
- Foods that rapidly increase the concentration of blood glucose should be removed. This food is high in starch, sugar, fructose.
- Reduces the total calorie content. The energy value of meals is equal to the number of calories burned.
- It is necessary to observe six meals a day.
With diabetes, it is important to eat regularly. If the patient adheres to a diet, then only this can improve the patient’s condition. With a mild form of the disease, only nutritional correction is dispensed with.
Low-calorie foods are preferred. They should be rich in protein, plant fiber and dietary fiber.
Limit foods containing a large amount of animal fats, fast carbohydrates, fructose. Remove all foods with a high glycemic index. Alcohol in diabetes is also prohibited.
Insulin therapy
The introduction of insulin is carried out according to the scheme recommended by the doctor. At the same time, the glucose level is systematically monitored. Insulins are produced in three types: short-acting, prolonged, intermediate.
The prolonged drug is administered once a day. Compliance with an individually selected scheme for the use of intermediate and short insulin allows you to achieve compensation for the disease.
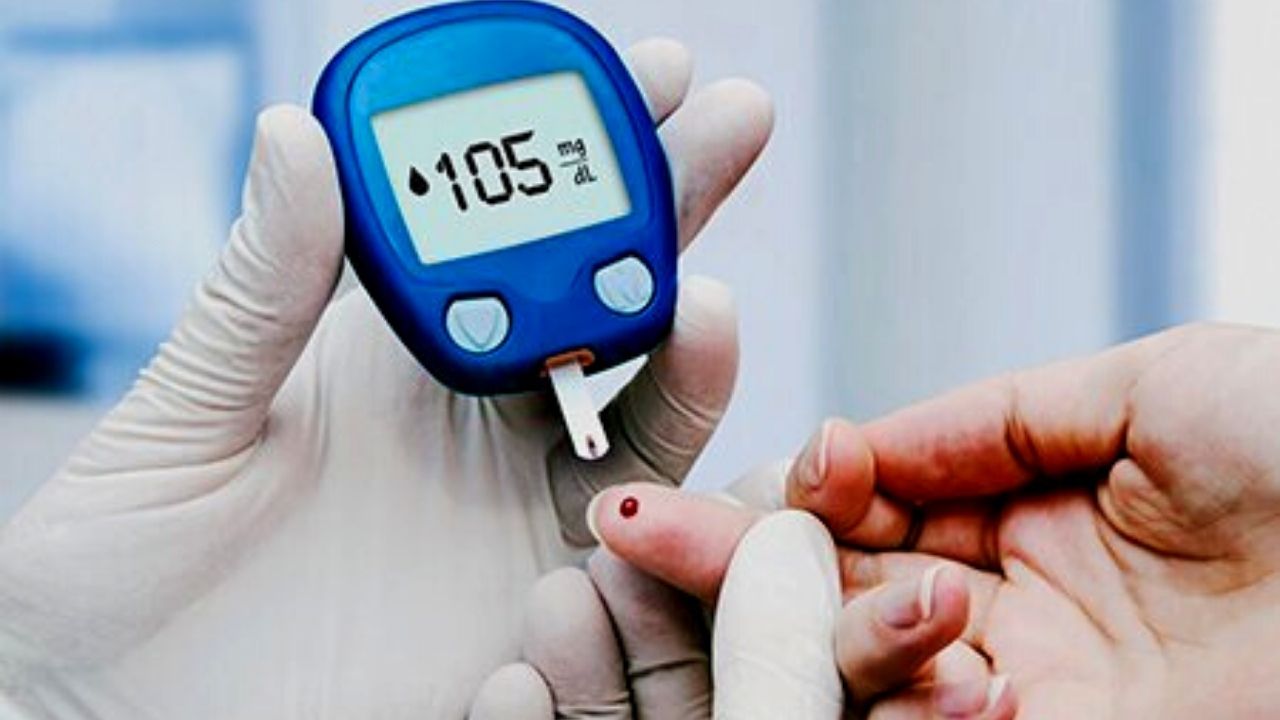
Self-monitoring of glycemic levels
Self-monitoring of blood glucose is performed daily. Modern blood glucose meters allow you to do this anywhere – at home and at work at a convenient time. The device helps you create a balanced diet, develop an exercise plan, and determine the timing of insulin delivery and medication. The measurement detects hypoglycemia and helps to maintain the glucose concentration in the normal range.
Sugar-lowering drugs
Sugar-lowering drugs in tablets are prescribed for type 2 diabetes as an addition to the diet. There are such groups of drugs:
- sulfonylurea derivatives – stimulate pancreatic insulin secretion, facilitate the penetration of glucose into cells;
- biguanides – reduce the absorption of glucose in the intestinal wall;
- meglitinides – reduce sugar levels, stimulate insulin secretion;
- alpha-glucosidase inhibitors – slow down the rise in sugar levels by inactivating enzymes for the absorption of starch;
- thiazolidinediones – reduce the amount of sugar released from the liver cells, improve the sensitivity of cells to insulin.
With diabetes, it is important to monitor the patient’s well-being and condition in order to avoid sudden changes in glucose levels.
Prevention of diabetes mellitus
Patients with diabetes mellitus need to be constantly monitored by an endocrinologist – he will help organize the correct lifestyle, diet and the necessary treatment. It is important to avoid the development of acute and chronic complications. Patients with type I diabetes are advised to increase the body’s resistance to infections, and patients with type II are advised to prevent the development of obesity.
Outlook
Diabetes mellitus is classified as a serious illness. If untreated, serious life-threatening complications develop. If symptoms of high blood sugar appear, you should consult a doctor and not self-medicate.