Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease that is caused by an infection with bacteria (gonococci). An inflammation of the sexual and urinary organs with purulent discharge from the urethra is typical for gonorrhea. But gonorrhea also affects other parts of the body. The use of condoms drastically reduces the risk of contracting gonorrhea. Here we will talk about symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment and can gonorrhea be cured?
ICD codes for Gonorrhea disease: A54
Brief overview
- Symptoms: Burning pain when urinating, discharge from the urethra (in men), purulent or bloody discharge from the vagina, conjunctivitis in the case of an infection of the eyes, more rarely general symptoms such as fever, joint pain, skin rash. Symptoms don’t always appear.
- Causes and risk factors: Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium, direct contact of the mucous membrane (e.g. of the penis, vagina, rectum, mouth and throat, eyes) with an infected person, e.g. through unprotected sexual intercourse, rarely infection of newborns during birth from an infected mother.
- Diagnosis: Detection of the gonorrhea pathogen by a smear, creation of a bacterial culture, test for antibiotic resistance.
- Treatment: Administration of two different antibiotics at the same time (so-called dual therapy), therapy of the infected person and their sexual partners.
- Prognosis: the prognosis is good if treated in good time; If left untreated, there is a risk of long-term effects such as adhesions and adhesions of the internal genital organs, infertility, abdominal pain, narrowing of the urethra, blindness (very rare today).
- Prevention: Consistent use of condoms reduces risk.
What is gonorrhea?
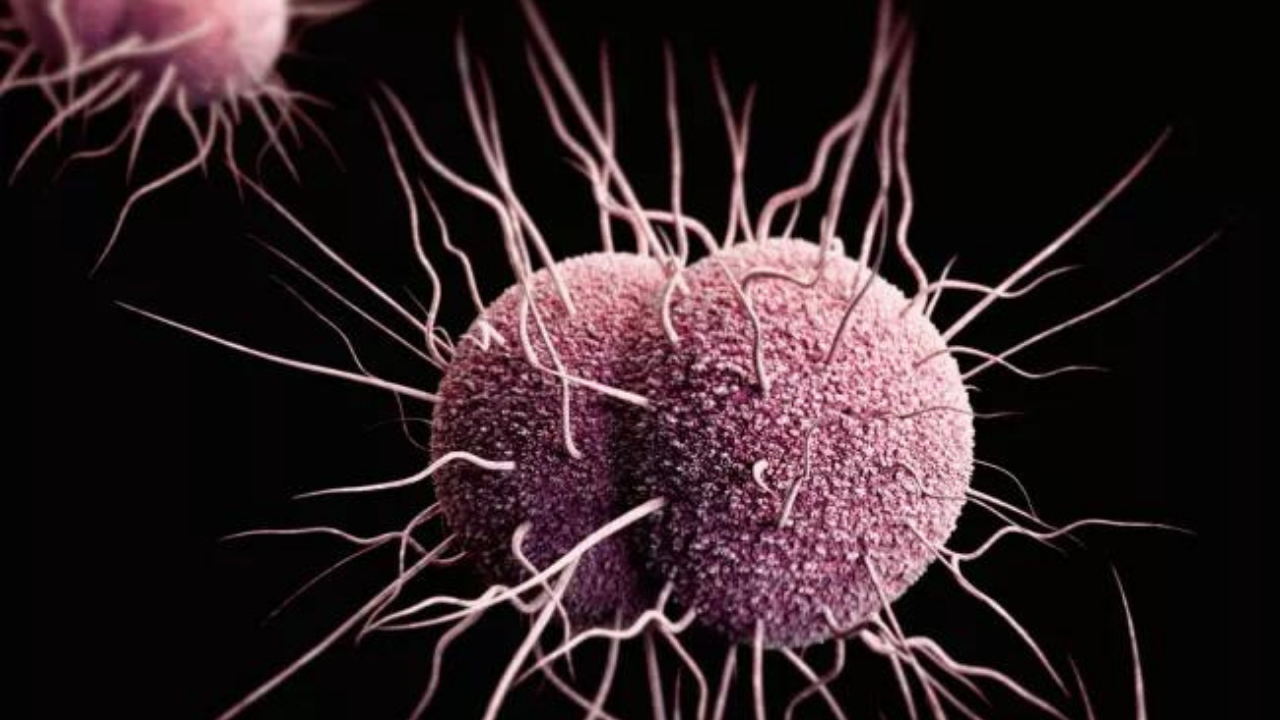
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease (STD). Gonorrhea is therefore one of the sexually transmitted diseases. The cause of gonorrhea are bacteria, so-called gonococci (Neisseria gonorrhoeae). The dermatologist Albert Neisser discovered the pathogen in 1879.
Gonorrhea leads to inflammation of the genital organs and the urinary tract. A purulent discharge from the urethra is typical of gonorrhea in men. In female, the symptoms are usually much weaker, so gonorrhea often goes undetected in female.
If left untreated, there is a risk of gonococci spreading throughout the body. Gonococcal infection occurs through unprotected sexual intercourse (genital, oral, anal) with an infected person.
Infection of the child during birth by the mother is also possible. The pathogens then cause purulent conjunctivitis (gonococcal conjunctivitis) in the newborn, which usually spreads to the cornea of the eye without treatment.
This form of gonorrhea used to be the most common cause of blindness in children in the western world (“neonatal blennorrhea”). To prevent this, a one percent silver nitrate solution was dripped into the eyes of the newborns.
Doctors today treat newborn babies with gonococcal infection with antibiotics given by injection to the children. Such treatment of infants is rarely necessary, as pregnant women are also checked for gonorrhea as part of the preventive medical check-ups.
Occurrence and frequency of gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is common all over the world. Only people get this sexually transmitted disease (STD). According to estimates by the World Health Organization (WHO), gonorrhea is the third most common sexually transmitted disease with around 87 million new cases per year.
The number of gonorrhea has been falling for a number of years. However, an increase in the incidence of gonorrhea has been observed since the mid-1990s. Young adults between the ages of 15 and 25 are particularly affected by gonorrhea, with men and women becoming ill.
However, if the doctor detects strains of pathogens that are resistant to certain antibiotics, he is obliged to report the infection to the health department.
What are the symptoms?
Typical gonorrhea symptoms in the early stages are inflammation of the urinary and genital organs and a purulent discharge from the urethra. In many cases, however, there are no symptoms of gonorrhea (silent infection).
Around every third infected man does not feel any symptoms from the disease. In women, gonorrhea is even more common with little or no symptoms: around half of infected women notice no typical symptoms.
The problem: if you don’t have gonorrhea symptoms, you usually don’t know that you have an infectious disease. Thus, gonorrhea is often passed on unknowingly. This means a high risk of the undetected spread of gonorrhea.
The time from gonococci bacteria infection to the appearance of the first symptoms (incubation period) is between one and a maximum of 2 weeks for gonorrhea, but the symptoms usually show up after two to seven days. A distinction is made between acute gonorrhea symptoms and chronic complaints.
Acute gonorrhea symptoms in men
- Burning pain when urinating (dysuria). In extreme cases, a feeling of “glass splinters in the urethra” arises. Symptoms are caused by inflammation of the urethra (urethritis).
- Painful swelling and redness of the penis and foreskin
- Purulent discharge from the urethra. Initially, only small amounts are produced, which are slimy. The amount increases very quickly, however, and the discharge looks yellowish-creamy.
- If there is no treatment, the bacteria rise into the male genital organs and cause inflammation of the prostate or epididymis there, for example .
- During anal intercourse, there is a possibility that gonorrhea can cause inflammation in the rectum (rectal gonorrhea). It manifests itself, for example, through slimy-purulent additions in the stool and pain when defecating.
- When infected through oral sex, gonorrhea symptoms can sometimes occur in the mouth. More precisely, the result is an inflammation of the throat with a sore throat (pharyngeal gonorrhea). However, an infection of the throat with gonorrhea causes no symptoms in 90 percent of cases.
Acute gonorrhea symptoms in women
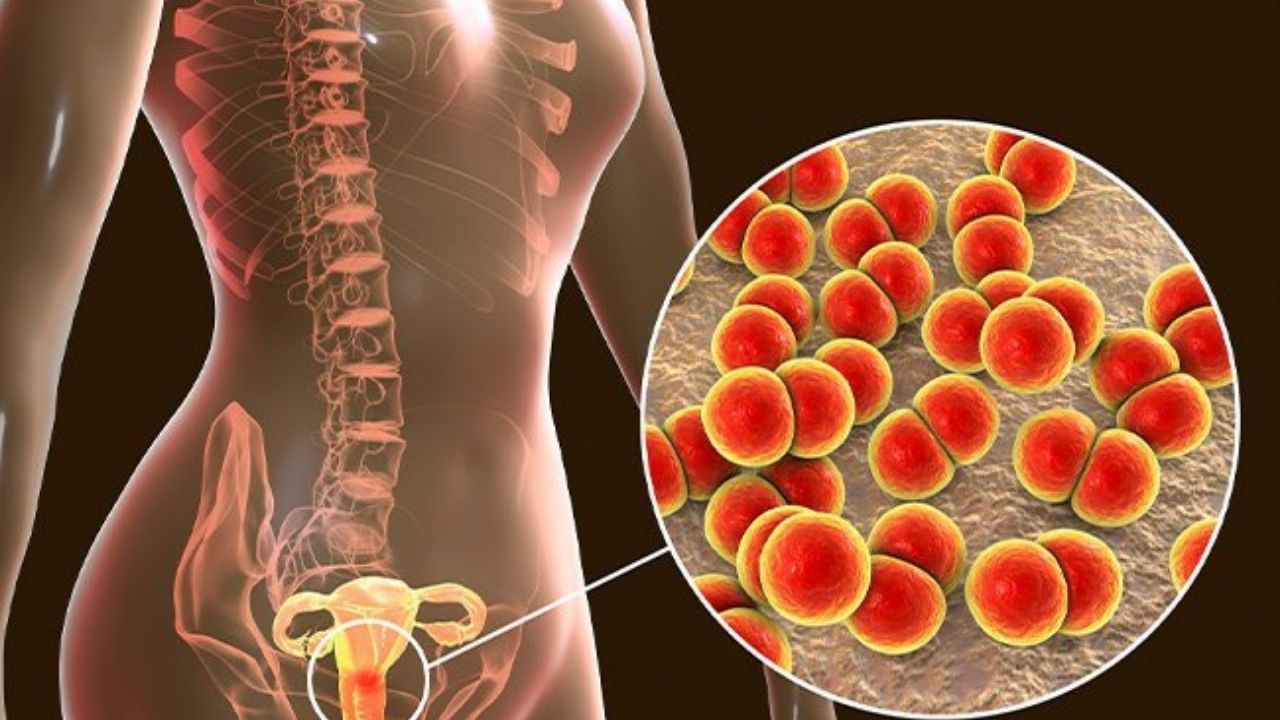
- In the early stages, symptoms of gonorrhea are usually very mild. Vaginal discharge and a slight burning sensation when urinating are possible. The discharge from the vagina can smell foul.
- An inflammation of the cervix (cervicitis) shows, for example, a purulent or bloody discharge.
- Sometimes gonorrhea spreads further to the internal genital organs, which in some cases leads to inflammation of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. This results in fever, abdominal pain, discharge and spotting.
- Often rectal gonorrhea in women occurs when the pathogen spreads from the genital tract to the rectum (secondary infection).
Without treatment, there is a risk of gonorrhea symptoms becoming chronic. The local symptoms on the mucous membranes mostly disappear, but the pathogens penetrate deeper tissue layers, where they usually cause chronic inflammation.
In men, chronic inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis) and / or inflammation of the epididymis (epididymitis) occurs more often. The production of pus is low. A droplet of pus forms only overnight, which typically flows out of the urethra before the first urination in the morning. The chronic inflammation is difficult to access for antibiotics and may lead to constrictions in the urethra.
In women, chronic gonorrhea often leads to far-reaching complications: If the bacteria rise in the female sexual organs, there is a risk of inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries (adnexitis). As a result, in some cases the fallopian tubes stick together and lead to sterility.
In addition, there is a higher risk of an ectopic pregnancy due to sticky fallopian tubes. In some women, the symptoms get worse during menstrual bleeding.
In both sexes, there is rarely the possibility that the pathogens can spread throughout the entire organism and cause gonorrhea symptoms in other parts of the body as well.
About two to three weeks after the infection, gonorrhea symptoms appear with fever, skin changes (such as rash or punctiform hemorrhages), painful inflammation of the joints and tendinitis. Doctors also speak of disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI).
Only in rare cases are the meninges (meningitis) and the heart (endocarditis). If gonorrhea is present during childbirth, the newborn may develop an infection of the conjunctiva in the eyes (“neonatal blennorrhea”).
Gonococcal infections of the eyes are also occasionally found in adults. Mostly it is a question of “carried away” bacteria in people with an existing genital gonorrhea infection. Inflammation of the eye (gonococcal ophthalmia) in adults is highly acute and usually has a worse course than in newborns.
If you suspect gonorrhea symptoms in yourself or your partner, do not be afraid to see a doctor!
Can gonorrhea be cured?
The question often raised in the minds of millions of people around the world is whether can gonorrhea be cured?
Yes, Usually gonorrhea is curable. the right treatment can cure gonorrhea disease. It is important that you take all of the medicine your doctor gives you to cure your gonococci infection.
Although medicine will stop the gonococci infection, it will not undo any permanent damage caused by the gonorrhea disease.
How do you get infected?
The cause of gonorrhea is an infection with the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonococci). Gonorrhea is primarily transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse (vaginal, oral, anal intercourse) with an infected person, more rarely during the birth process. This makes gonorrhea one of the sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
Transmission occurs when body fluids containing bacteria come into direct contact with the mucous membrane (such as the urethra, vagina, cervix), rectum, throat, conjunctiva). The bacteria then multiply at the site of the infection and trigger inflammation there. Without treatment, the pathogens spread further in the body. Outside the human body, gonococci perish very quickly.
If a pregnant woman has gonorrhea, there is a high risk that the baby will be infected during the birth process. Typically, conjunctivitis (gonococcal conjunctivitis) occurs in the child. If left untreated, the infection spreads to other areas of the eye, such as the cornea, and in some cases leads to blindness (“neonatal blennorrhea”).
In pregnant women with a known gonococcal infection, the newborn is given antibiotics. General treatment of newborns is not required. Usually, checkups during pregnancy rule out infections such as gonorrhea (and other sexually transmitted diseases).
Especially in women, the symptoms of gonorrhea are often very mild and difficult to recognize. This runs the risk of spreading the infection unnoticed. People who offer or use sexual services, as well as people with frequently changing sex partners, have a higher risk of contracting gonorrhea.
Infections are also believed to be more common in men who have sex with men. However, the risk of contracting gonorrhea is particularly high with unprotected sexual intercourse of any kind.
Diagnosis of gonorrhea
A specialist in skin and sexually transmitted diseases is the right contact if you suspect gonorrhea. These doctors are called “venereologists”. Your family doctor or gynecologist are also a possible first point of contact if you suspect gonorrhea.
If there is a purulent discharge from the urethra or vagina, an examination is always useful. It is important that all partners of infected people or people with unclear inflammatory abdominal complaints have themselves checked for gonorrhea or other sexually transmitted diseases.
For sexually active men with inflammation of the testicles or epididymis, it is also advisable to be checked for an infection with gonococci.
The diagnosis of gonorrhea is made by detecting the pathogen (gonococci). To do this, the doctor takes a smear from the relevant area, such as the urethra, the cervix, the throat, the anus or the conjunctiva. He then examines the sample under the microscope.
In order to make a reliable diagnosis, the laboratory also produces a culture of the pathogen: To do this, the gonococci are transferred from the smear to a suitable nutrient medium. The pathogens multiply there and can then be reliably detected.
For an effective gonorrhea therapy, different antibiotics are tested for their effectiveness in the bacterial culture (antibiogram). This shows which antibiotics the gonococci are sensitive to and which active ingredients are ineffective.
In the past few years, bacteria that were resistant to the usual antibiotics (antibiotic resistance) could be detected again and again.
For gonorrhea infected people without symptoms (asymptomatic), test procedures based on a laboratory reproduction of the bacterial genome (PCR, polymerase chain reaction) are more accurate than bacterial cultures. Even if there are no complaints, it is possible for other people to be infected.
Treatment for gonorrhea?
Antibiotics are suitable for gonorrhea therapy. In the past, primarily penicillin was used to treat gonorrhea. Penicillin-resistant gonococcal strains from Asia and Africa have appeared more frequently in recent years. Therefore, doctors are now using other antibiotics to treat gonorrhea.
In most cases, two different antibiotics (ceftriaxone and azithromycin) are used in combination. In special cases, for example for the treatment of gonorrhea during pregnancy, the doctor only uses one antibiotic.
In most cases of gonorrhea, the gonococci die within 24 hours of administration of the effective antibiotics and are then no longer detectable. Nevertheless, it is important not to end gonorrhea therapy too early: This promotes the development of resistance – and resistant germs are difficult to treat.
All sexual partners of those infected with gonorrhea should be examined and treated if necessary. This applies to the sexual contacts within two weeks before the onset of symptoms.
If a gonorrhea infection was discovered by chance without symptoms, it is recommended that all sexual partners have undergone gonorrhea therapy within the last 90 days. During and up to seven days after therapy, it is important for all those affected to refrain from unprotected sex.
Newborns with purulent conjunctivitis caused by gonorrhea are given a single dose of antibiotics as an injection into the muscle (intramuscular) or into the vein (intravenous). In addition, the eyes and conjunctiva should be rinsed regularly with saline solution.
Antibiotic resistance
According to estimates by the World Health Organization (WHO), gonorrhea will probably pose great problems for mankind in the coming years. The reason for concern is the observation that some gonococcal strains have become resistant to the usual antibiotic therapy for gonorrhea (antibiotic resistance).
For this reason, experts are already recommending dual therapy for gonorrhea, i.e. with a combination of two antibiotics. A preparation alone no longer offers sufficient security for the success of the treatment. More and more completely resistant gonococcal strains are found worldwide, especially in Asia.
Course of the disease and prognosis
can gonorrhea be cured? – If you also had this question, so answer is yes. As we have mentioned above that. Usually gonorrhea is curable and has a good prognosis: if gonorrhea is treated in good time, you do not have to expect any long-term effects.
However, if gonorrhea is left untreated, health consequences are likely. The long-term effects of gonorrhea include chronic inflammation of the internal genital organs with persistent pain, sticking of the egg or spermatic ducts and thus infertility. Therapy is therefore very important.
Without treatment, the gonorrhea pathogens can spread through the bloodstream throughout the body in very rare cases. Doctors speak of a DGI (disseminated gonococcal infection).
The consequences are inflammation of the joints and tendons, characteristic rashes with red pustules or small hemorrhages (petechiae), fever and chills.
In severe cases, the disseminated gonococcal infection is followed by inflammation of the meninges (meningitis) and inflammation of the lining of the heart (endocarditis).
Prevention
Consistent use of condoms can prevent the risk of gonorrhea.
