Contact dermatitis eyelid is an inflammatory lesion of the skin of the eyelids. The main symptoms of the disease are burning, itching, specific rashes, hyperemia and edema. To make a diagnosis, laboratory (ELISA, PCR, IgE level determination, complete blood count, histological examination of a biopsy) and instrumental research methods (biomicroscopy) are used. Depending on the etiology of the disease, treatment tactics are reduced to the use of antibacterial agents, H2-histamine blockers, glucocorticosteroids, antiviral drugs or calcineurin inhibitors.
General information
Contact dermatitis eyelid is a common pathology in which there is an isolated lesion of the eyelid skin or its combination with similar skin manifestations of other localizations. According to statistics, every tenth person during his life noted symptoms of contact dermatitis eyelid, In the structure of the general incidence of dermatitis, the eyelids and the periorbital region are affected in 27% of cases.
Usually the upper eyelids are involved in the pathological process. The seborrheic form often develops in young women, which is associated with vegetative neurosis. There are no epidemiological data on the prevalence of the disease. Usually the upper eyelids are involved in the pathological process. The seborrheic form often develops in young women, which is associated with vegetative neurosis. There are no epidemiological data on the prevalence of the disease.
Symptoms of contact dermatitis eyelid
With a herpetic origin, the disease develops sharply. Against the background of hyperemia of the skin of the face and eyelids, small bubbles appear, filled with transparent contents. Patients note that specific elements of the rash are formed against the background of general hyperthermia. Their formation is preceded by a burning sensation and itching in the periorbital zone.
Over time, dry crusts form in place of the bubbles, which disappear without a trace after 2 weeks. The herpetic form is characterized by a high tendency to relapse. If the etiological factor is infection with the herpes zoster virus, then the clinical picture is dominated by complaints of severe pain in the area of the rash. Elements of the rash are located along the nerve fibers.
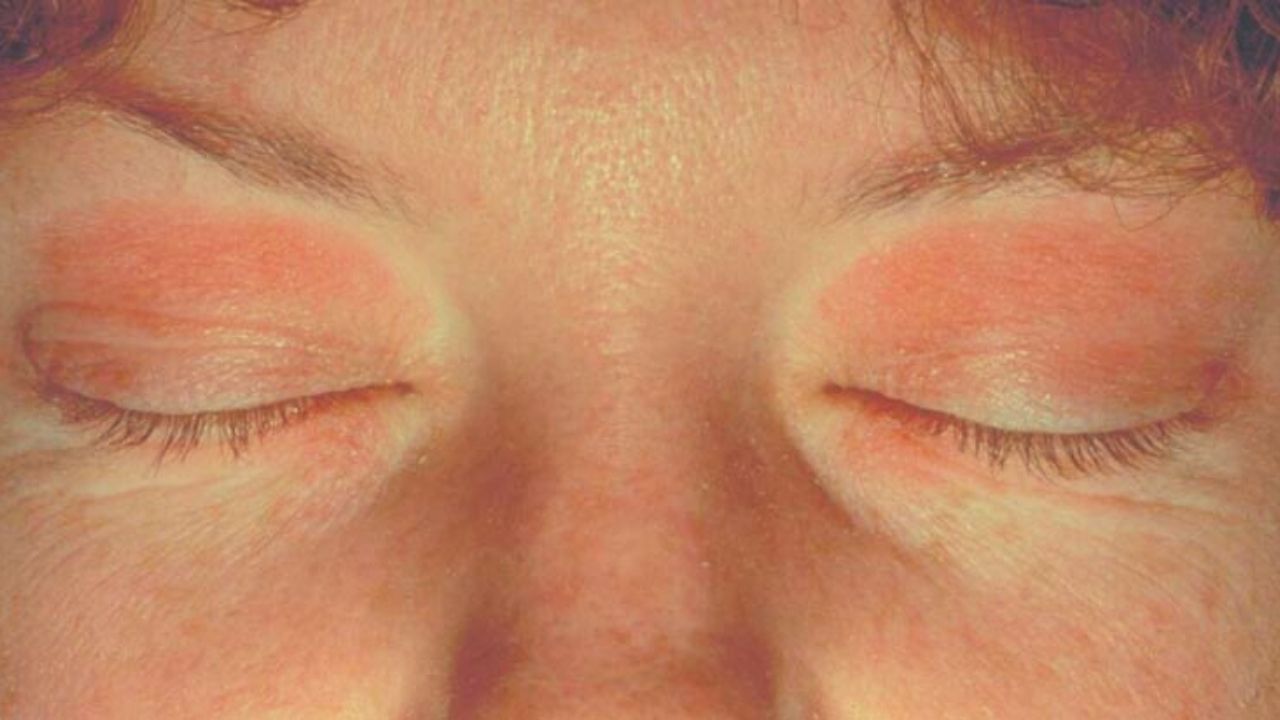
With allergic dermatitis, patients complain of swelling and hyperemia of the palpebral region. A vesicular, rarely bullous rash is found on the skin. Due to severe swelling, the patient often cannot open his eyes. In the corners of the palpebral fissure, maceration of the skin is observed.
With a delayed version of hypersensitivity, the skin gradually thickens and becomes drier. Further, a spotty or papulovesyculosis rash appears. With a severe course of the allergic process, angioedema of the periorbital zone (Quincke’s edema) develops, often spreading to the surrounding tissues: nose, lips, cheeks.
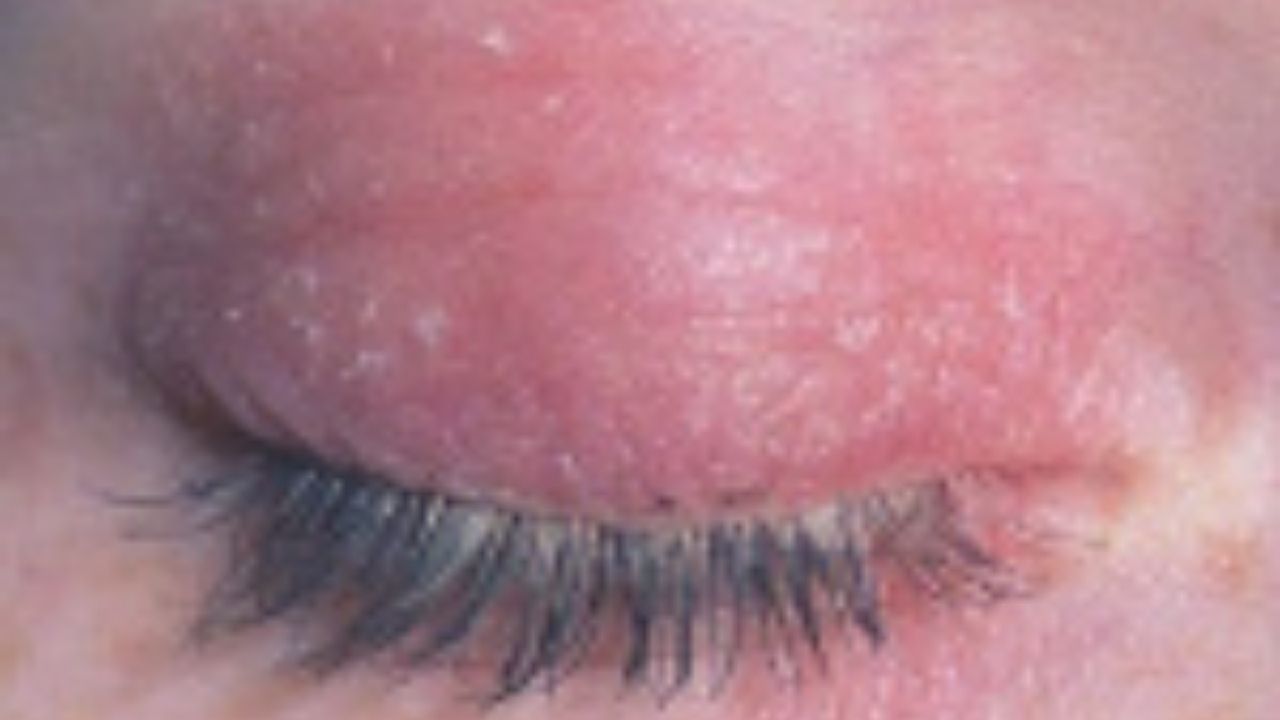
With a seborrheic origin of the pathology, patients note an oily sheen, peeling of the skin and loss of eyelashes. The stratum corneum of the epidermis is thickened. Itching occurs early. The first is the anterior palpebral edge, which is due to the location of the sebaceous glands at the roots of the eyelashes.
Further, signs of dermatitis are detected in the area of the cheekbones, wings of the nose, and forehead.
Often, the pathological process extends to the scalp. For atopic dermatitis of the century, the appearance of foci of hyperpigmentation is characteristic. In children, an additional fold of the lower eyelid is often formed (Denier-Morgan symptom).
Causes of contact dermatitis eyelid
Inflammation of the skin of the eyelids and periorbital region is a pathological reaction that occurs in response to the effects of many exogenous and endogenous factors. It is not always possible to establish the etiology. In childhood, atopic reactions play a leading role. The main reasons for the development of pathology:
- Infectious diseases. Most often, the onset of symptoms of dermatitis is associated with infection with herpes simplex virus or herpes zoster virus. Secondary inflammation of the skin is detected in patients with measles , chickenpox , scarlet fever .
- Allergic reactions. In the role of allergens are medicines, food, pollen, animal hair, etc. Inflammatory manifestations are found in other parts of the body. Local lesion of the eyelids is typical for allergy to cosmetics.
- Exposure to physical factors. The disease can be the result of excessive sun exposure or reaction to cold. Cases of radiation injury caused by ionizing radiation are also described.
- The influence of chemicals. Pathological changes develop in case of accidental contact with household chemicals on the skin or due to prolonged contact of the eyelid skin with chemicals in a production environment if safety precautions are not followed.
- Dysfunction of the sebaceous glands. The enhanced production of sebaceous glands of sebum creates favorable conditions for the occurrence of seborrheic dermatitis.
Pathogenesis of contact dermatitis eyelid
When infected with the herpes simplex virus, the appearance of clinical symptoms is due to the dermato-, meso- and neurotropic action of the pathological agent. In patients with a history of droplet infections (measles, chickenpox, scarlet fever), dermatitis is a secondary pathology that develops due to the addition of bacterial flora or an atopic reaction to local antiseptics.
In the pathogenesis of the seborrheic form of the disease, the leading role is given to the violation of the nervous and neuroendocrine dysfunction of the sebaceous glands. Often the first symptoms occur against the background of hormonal imbalance, including hormonal changes in puberty.
The allergic variant of the disease is caused by an immediate or delayed hypersensitivity reaction, which is determined by the type of sensitization of the body. With the immediate type, the signs are detected 15-30 minutes after the trigger is exposed and completely disappear after 1-2 hours. With a delayed type, clinical symptoms develop after 6-12 hours, external changes are leveled only after a few days or weeks.
The skin of the palpebral zone is most sensitive to the adverse effects of physical factors. This is due to the anatomical and physiological structural features (thin musculocutaneous and conjunctival-cartilaginous layers).
Complications of contact dermatitis eyelid
A complicated course is characteristic of the formation of pustules and vesicles on the skin of the eyelids. The opening of the vesicles is often accompanied by their infection.
Acute blepharitis and blepharoconjunctivitis are common outcomes. The formation of erosive defects is complicated by the formation of dense keloid scars and eyelid deformation.
Patients note a violation of the function of closing the orbital fissure. Individuals with dermatitis are at risk of developing inflammatory complications of the anterior segment of the eyes (keratitis, keratoconjunctivitis). In rare cases, the formation of an abscess of the eyelid is observed.
Diagnosis of contact dermatitis eyelid
If contact dermatitis eyelid is suspected, a physical examination is performed, and specific diagnostic methods are prescribed. With the help of biomicroscopy of the eye using a slit lamp, hyperemia, swelling of the eyelids and pathological rashes are determined, the nature of which depends on the etiology of the disease. In the presence of herpetic vesicles, their puncture is shown with further microscopic analysis of the contents. Laboratory research methods include:
- Complete blood count (CBC). With the viral nature of the pathology, a shift of the leukocyte formula to the right is found. The bacterial origin of the disease is evidenced by the shift of the formula to the left. ESR level is above normal.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The study is used for the infectious nature of the disease. The Ig M titer is increased 4 or more times, which indicates an acute form of pathology. An increase in the Ig G titer indicates a chronic course.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The method makes it possible to identify the genetic material (DNA, RNA) of the pathogen in the blood. This is the most informative technique for the viral origin of dermatitis.
- Determination of immunoglobulin E in the blood. IgE is an immediate type hypersensitivity marker. An increase in its titer in serum indicates the development of an allergic reaction.
- Histological examination. Biopsy histology is carried out with seborrheic lesions. Follicular plugs, perivascular infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes and histiocytes are visualized.
Treatment for contact dermatitis eyelid
The therapeutic tactics are determined by the etiology of the disease. In the herpetic form, the bubbles on the eyelids are lubricated with an ointment containing acyclovir. Medicines should be applied when the first clinical symptoms appear. In addition to local treatment, the administration of immunotherapeutic drugs (recombinant interferon, immunomodulators) is indicated.
The duration of the course is 10-14 days. 1-2 months after the relief of symptoms, the introduction of the herpes vaccine is recommended to achieve a stable remission.
The first stage in the treatment of allergic dermatitis is the elimination of the etiological factor. Patients are shown the use of antihistamines. Corticosteroid ointments are applied to the skin of the eyelids. In case of a complicated course, hormonal agents are prescribed in a short course. With seborrheic genesis of the disease, topical glucocorticosteroids are used in combination with calcineurin inhibitors.
In the case of a pronounced inflammatory reaction, anti-inflammatory drugs are used in the form of lotions. To prevent the development of bacterial complications, 1-2% alcohol solutions of aniline dyes are applied to the palpebral zone. With severe itching, H2-histamine blockers are additionally indicated.
Forecast and prevention of contact dermatitis eyelid
With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable. Specific preventive measures have not been developed, non-specific ones are aimed at preventing contact with the etiological factor. When working with industrial chemicals, you must use personal protective equipment (goggles, mask).
Patients with a history of recurrent herpes infection with the development of the first symptoms (itching, burning) should be applied to the eyelid with the drug, without waiting for the appearance of a rash. With a seborrheic nature, the focus should be on correcting hormonal dysfunction.