Ischemic heart disease (Coronary heart disease) is a functional and organic damage to the myocardium, which is provoked by a lack or complete cessation of blood supply. Pathology can manifest itself as acute and chronic conditions, including angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, etc. Symptoms of the disease are determined by its form. Moreover, Ischemic heart disease is the most common cause of sudden death today.
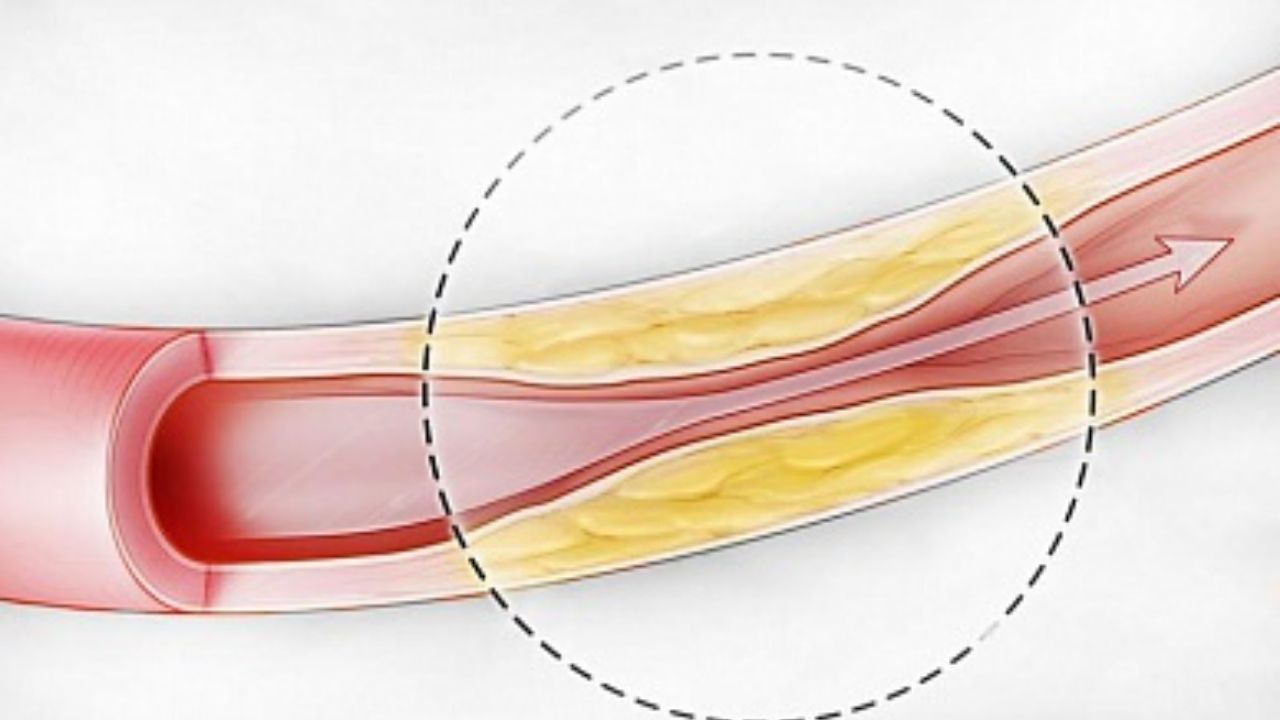
Causes of ischemic heart disease
In most cases, the main cause of the development of pathology is atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries. It can be expressed both in a slight narrowing of the lumen due to its filling with plaque, and in its complete overlap.
Also, Ischemic heart disease can occur against the background of spasm of the coronary arteries or thromboembolism. These pathologies also usually develop against the background of atherosclerotic lesions.
Risk factors
All risk factors are divided into two main groups.
Immutable factors :
- Age. Patients over 50 are susceptible to coronary heart disease
- Weighed down heredity. Persons whose close relatives have been diagnosed with atherosclerosis are at risk of developing coronary artery disease.
- Floor. As a rule, men suffer from pathology
Variable factors :
- Lack of physical activity
- Overweight and metabolic disorders
- Long-term high blood pressure that has not been corrected with drugs
- Dyslipidemia. This pathology is characterized by an imbalance between high and low density lipoproteins.
- Bad habits. First of all, this is long-term smoking, but alcohol consumption (especially in large doses) negatively affects the state of the myocardium.
- Eating disorders. People who abuse fatty foods with a large amount of simple carbohydrates and overeat in general are at risk of developing coronary artery disease.
- Associated violations. These include long-term hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus.
Development mechanisms
Heart disease is caused by an imbalance between a muscle’s demand for blood supply and actual blood flow. It can develop due to an increased need for the myocardium for blood supply or with the usual need, but reduced blood circulation. Deficiency of blood supply is especially pronounced with a decrease in coronary blood flow.
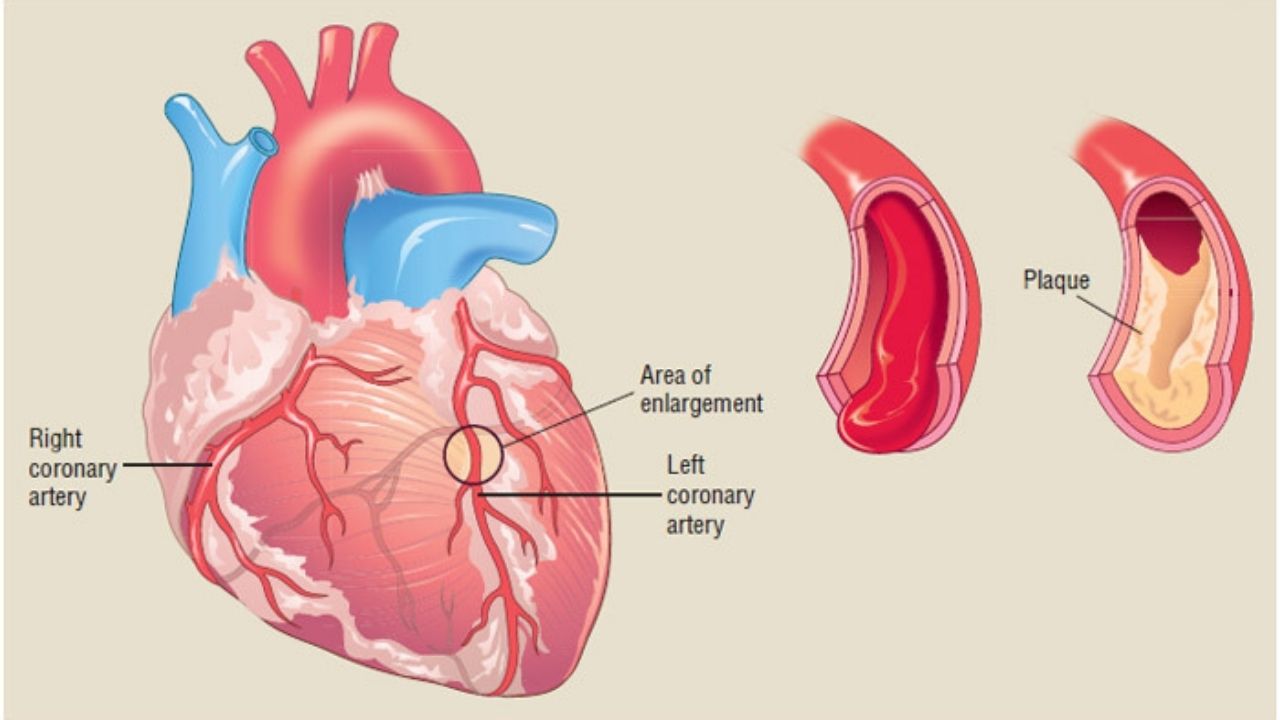
Types of Ischemic heart disease
There are the following types of coronary heart disease:
- Sudden coronary death
- Angina pectoris . Allocate angina pectoris, stable, unstable and spontaneous
- Violations of the rhythm and conduction of the heart
- Painless form
- Myocardial infarction : small or large focal
- Postinfarction cardiosclerosis
- Heart failure
Sudden coronary death is especially dangerous. It can come on instantly or develop within 6 hours. It is also called primary cardiac arrest. The condition is unexpected. It is based on electrical instability of the myocardium. The danger of this condition is associated with an increased risk of death.
The most common manifestation of Ischemic heart disease, which necessarily requires treatment, is angina pectoris. It manifests itself as pains behind the sternum of a squeezing and pressing character, which can be given to the shoulder, left hand and even to the lower jaw. Usually, the discomfort is relieved by rest. Signs of angina pectoris, as a rule, occur in the cold, after physical exertion, with high blood pressure, after food abuse, as well as with pronounced emotional stress. The attack usually lasts no more than a few minutes. Progressive angina is diagnosed when a patient’s exercise tolerance decreases. Gradually, the patient can tolerate it worse and worse. Some people are diagnosed with resting angina, which occurs predominantly at night.
Treatment of coronary heart disease with various symptoms should be carried out after the first attack. The main goal of therapy is to restore blood flow to the myocardium and prevent the development of complications. The cardiologist will have to select the necessary medications: antihypertensive drugs, statins, beta-blockers, etc. Medicines are prescribed in accordance with the symptoms and causes of the development of pathology.
If necessary, an operation is prescribed. Today, patients are offered two main methods of restoring blood supply :
- Percutaneous stenting. This technique involves the restoration of the lumen of the vessel using a special frame (stent), which is installed inside
- Coronary artery bypass grafting. This operation is more complex and involves the installation of vascular prostheses in order to bypass the narrowing or complete blockage.
Also, complex therapy implies the patient’s adherence to a special diet, rejection of bad habits, a gradual increase in physical activity, and weight loss (if necessary). Due to the observance of simple recommendations, some patients are able to successfully lower blood pressure and reduce the concentration of cholesterol in the blood.
Diagnosis of Ischemic heart disease
Before starting treatment for ischemic heart disease, a comprehensive examination is mandatory.
Laboratory diagnostics :
- General blood and urine tests
- Blood chemistry
- Coagulogram
Instrumental examinations :
- ECG (electrocardiography), this technique is aimed at determining the heart rate and heart rate. As part of the examination, the cardiologist compares the patient’s indicators with normal ones and draws conclusions about the likelihood of the presence of pathology and its type
- CAG (coronary angiography). This technique is especially relevant in identifying coronary artery disease. As part of the examination, a special conductor is introduced into the patient’s body, which follows, under X-ray control, from the femoral artery. The contrast agent, which is visible under X-rays, allows you to quickly detect all anomalies
- Echo-KG (echocardiography ) . This technique is ultrasonic. It is aimed at studying the functionality of not only the heart, but also the coronary vessels and allows you to detect a number of pathologies
- Load tests . They are prescribed for the differential diagnosis of clinical forms of ischemic heart disease among themselves, as well as ischemic heart disease with other diseases. Relevant for determining the individual tolerance of physical activity, assessing the effectiveness of the treatment of heart diseases and assessing the ability to work
- Scintigraphy . It is carried out with the aim of visualizing the muscle, identifying factors in which the appearance of ischemic areas is possible
Patients are prescribed other examinations. The Holter testing technique is often used. It allows for round-the-clock monitoring of the heart and detects abnormalities that appear only under stress or at rest. There are other diagnostic techniques.
Important! The complex of examinations is determined by the doctor. In some cases, it is enough to undergo an ECG and take a blood test, in others, daily monitoring and a number of other complex studies are required.
Ischemic heart disease treatment
When the disease is detected in the early stages, an individual selection of the optimal complex drug treatment of ischemic heart disease is required, aimed at stopping the further progression of atherosclerosis, ischemic changes in the myocardium, correcting the manifestations of heart failure, reducing the ability of blood to thrombus, excluding risk factors.
When coronary artery disease is detected, it is necessary to determine the possibility of surgical treatment of Ischemic heart disease, aimed at mechanically improving blood flow through the coronary arteries:
- Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty with stenting. Intravascular low- traumatic operation, which consists in eliminating the narrowing of the coronary artery by inflating a special balloon at the site of narrowing under very high pressure (8-12 atmospheres) and reinforcing this area with a metal micro-frame (stent) put on the balloon
- Coronary artery bypass grafting in various modifications. Creation of a bypass path of blood flow in addition to constricted vessels, which allows you to provide the heart with oxygen and restore its function. As a new pathway for blood flow – a shunt – the patient’s own vessels are used, which move to the heart and are sutured above and below the narrowing of the coronary artery. For this, the radial artery (on the forearm), the internal thoracic artery (mammary-coronary artery bypass grafting) or the great saphenous vein of the lower limb (autovenous coronary artery bypass grafting) are used.
Coronary artery bypass grafting can be performed in various conditions:
- in conditions of artificial circulation with cardioplegia;
- on a beating heart without artificial circulation;
- on a beating heart with artificial circulation.
Coronary bypass surgery is also possible in the presence of complicated forms of coronary artery disease:
- with a reduced left ventricular ejection fraction;
- with mitral regurgitation;
- with left ventricular aneurysm;
- with atrial fibrillation.
This operation relieves the patient of angina attacks, restores exercise tolerance, and reduces the risk of sudden cardiac death and the development of myocardial infarction.
It is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner when the first signs of angina pectoris appear, when it is possible to stop the development of the disease and reduce the risk of a heart attack without surgery.