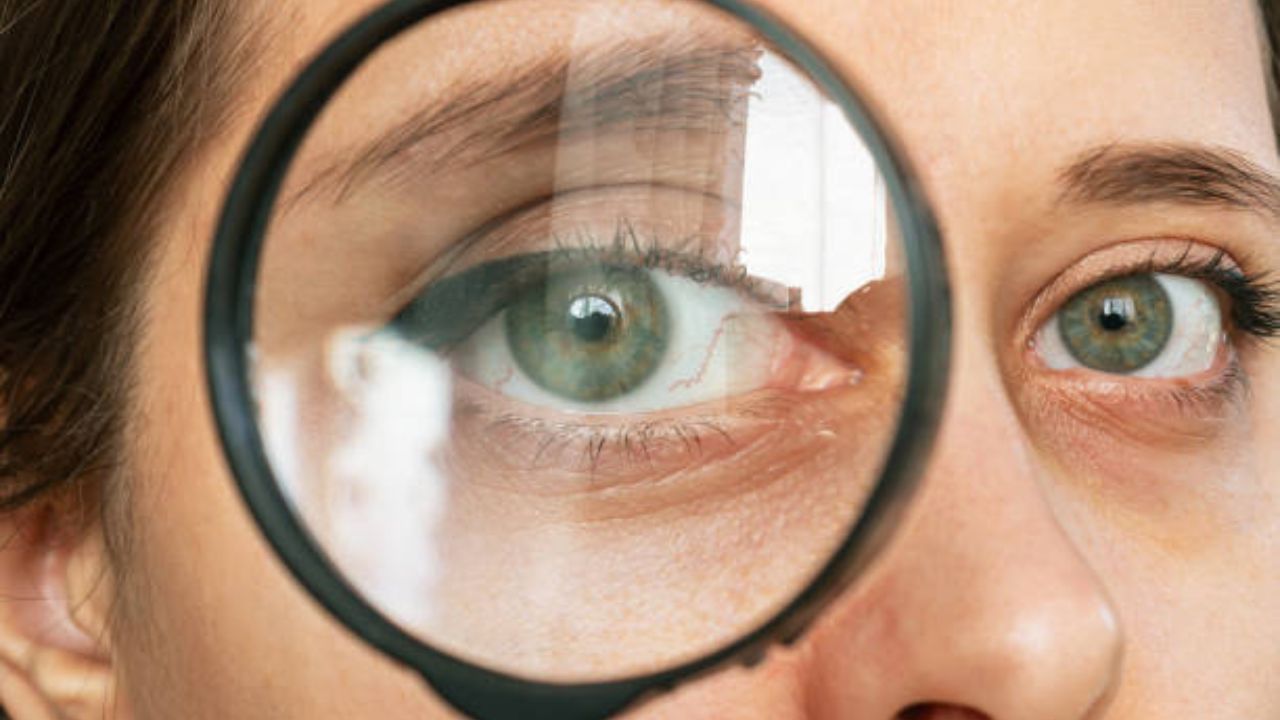
Punctate keratitis is an eye disorder caused by the death of small groups of cells on the surface of the cornea (the clear layer in front of the iris and pupil).
The eyes become red, watery and sensitive to light; You may lose some vision.
Keratitis is an eye condition that occurs when the cornea, the thin, clear tissue that lines the pupil and iris, becomes inflamed.
There are different types of keratitis depending on their cause: herpetic keratitis, bacterial keratitis, and punctate keratitis.
Punctate keratitis is a very common condition that often affects people who suffer from dry eyes or wear contact lenses incorrectly.
This type of keratitis causes very annoying symptoms and even blurred vision.
Punctate keratitis ICD 10: H16.14What is punctate keratitis?
Punctate keratitis is a disorder that occurs due to the death of small cell groups in the cornea, the tissue that lines the iris and pupil.
When examining the cornea, it can be noted that the tissue is inflamed and small lesions in the form of points are observed.
This condition is benign and most often affects people who suffer from dry eyes, use contact lenses incorrectly or are exposed to the sun without any type of protective glasses.
Causes of punctate keratitis
Punctate keratitis can be caused by various factors, among the most common are:
- Viral or bacterial infection, including trachoma.
- Eye dryness, better known as xerophthalmia.
- Splash in the eyes of very strong chemical products.
- Direct exposure to sunlight without protection.
- Wearing lenses for a long time or incorrectly.
- Inflammation of the eyelids or blepharitis.
- Allergy to eye drops.
- Side effect of certain medications.
- Peripheral facial palsy or Bell’s palsy.
Symptoms of punctate keratitis
Punctate keratitis usually causes eye pain, tearing, hypersensitivity to bright light, eye redness, and slightly blurred vision. There may often be a burning, gritty, or foreign body sensation in the eye.
The symptoms of punctate keratitis can be any of the following:
- Photophobia or hypersensitivity to light.
- Eye pain.
- Constant and excessive tearing.
- Redness of the eye.
- Blurred vision.
- Sensation of having a foreign body inside the eye.
- Burning.
- If punctate keratitis is caused by a virus, the lymph node in front of the ear is likely to be swollen.
When ultraviolet rays are the cause of the disorder, symptoms do not appear until several hours after exposure and last 1 to 2 days.
When the disorder is caused by a virus, the lymph node in front of the ear appears swollen and tender to the touch.
Symptoms can often be relieved with eye drops or ointments.
•∆• You may also like: Cataract : What You Need To Must Know
Diagnosis of punctate keratitis
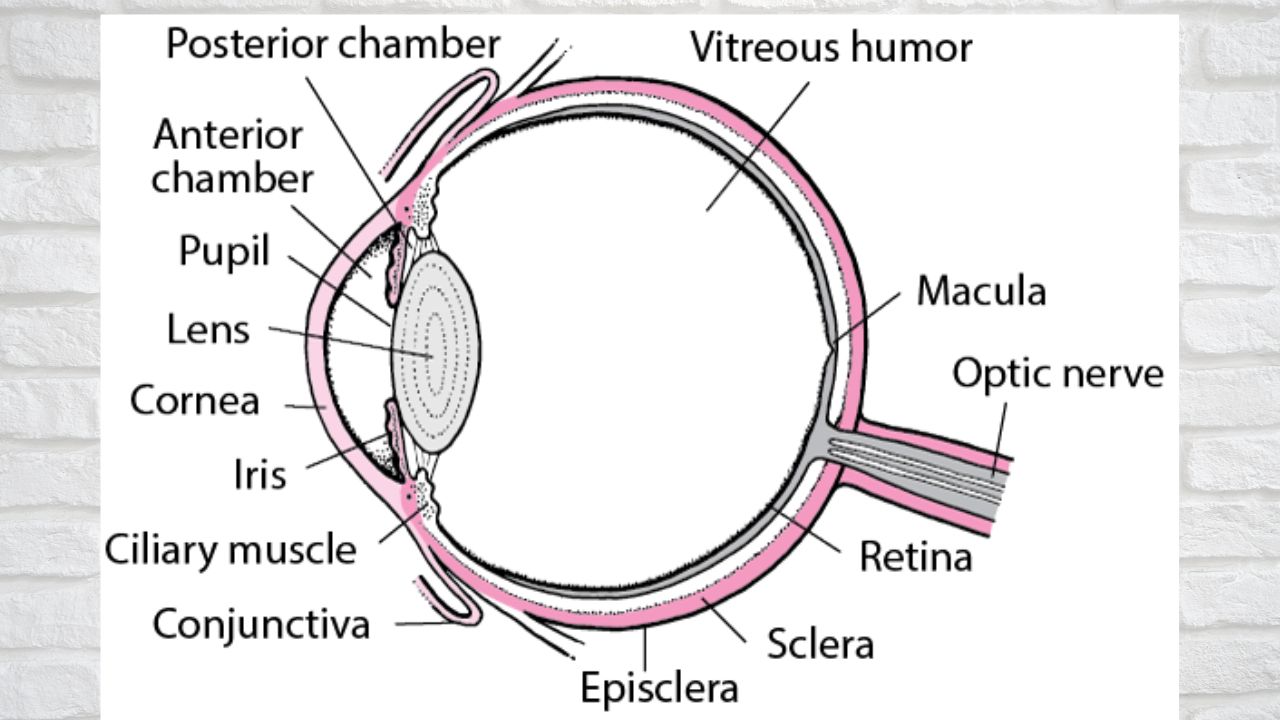
The diagnosis of punctate keratitis is based on the affected person’s symptoms and the results of an eye exam.
To receive a diagnosis of punctate keratitis, it is necessary for the person to go to an ophthalmological consultation to examine the cornea exhaustively.
The ophthalmologist will be able to determine if it is a punctate keratitis by examining the eye and discussing the symptoms with the patient.
Diagnosis of punctate keratitis is based on symptoms, determining if there has been exposure to any of the known causes, and examining the cornea with a slit lamp (an instrument that allows the eye to be viewed at high magnification).
During the examination, the doctor may apply eye drops that contain a yellow-green dye called fluorescein. Fluorescein temporarily stains damaged areas of the cornea, allowing damaged areas to be seen that would not otherwise be visible.
However, it is essential to inspect the cornea with a slit lamp, an instrument that allows precise observation of the tissue to evaluate its injuries.
During the eye exam, the ophthalmologist may apply drops to your eyes that contain a yellow dye known as fluorescein.
This substance stains corneal lesions and allows damaged areas to be seen that would be very difficult to detect due to the transparent tone of the cornea.
In a cornea affected with punctate keratitis, a yellow pointillism can be seen on the cornea, hence the name of this disease.
Treatment of punctate keratitis
The treatment of punctate keratitis can vary depending on its cause, let’s see:
- If punctate keratitis is caused by a bacterial infection, usually caused by improper use of contact lenses, it will be necessary for the patient to take antibiotic medications that can only be prescribed by the ophthalmologist. In addition, it is important to suspend the use of contact lenses until the doctor orders otherwise.
- When it has been a virus that has generated dotted keratitis, it is very likely that the doctor will not indicate any treatment. In these cases, the disease usually clears up on its own within three weeks.
- In cases of punctate keratitis due to dry eyes, it will be necessary to apply eye drops prepared with ingredients very similar to the components of real tears. In case the patient does not improve, the ophthalmologist will propose other treatments for dry eye. The goal is to keep the eye moist.
- Punctate keratitis caused by exposure to sunlight or ultraviolet light is treated through antibiotic ointments and drops that, in addition to treating the pathology, offer relief.
If the cause of the disorder is a reaction to a drug or irritation caused by an allergy to eye drops, the drug or eye drops should be discontinued.
Most people make a full recovery.
It is important to treat punctate keratitis as soon as possible for a complete recovery from the condition and its symptoms.
